Chart Mitosis In Animals
Original price was: KSh 1,101.00.KSh 680.00Current price is: KSh 680.00.
‘-laminated with 27 micron thick polyester film
-Renders the chart Tear,
-Water & Dust resistant.
-Language – English
-Size : 55 x 90 cm
- Description
- Reviews (0)
Description
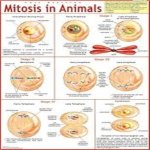
Chart Mitosis In Animals
This chart describes the process of mitosis in animals, it explains various concepts related to biology through illustrations including its phases and key components.
- Nuclear envelope
Prophase | Chromosomes condense and become visible. Centrioles migrate to opposite poles and start organizing spindle fibers. | – Nuclear envelope begins to fragment. – Centrioles, located near the nucleus, replicate and move towards opposite poles.
- Spindle fibers, made of microtubules, start to form between the centrioles. | – Chromosomes (condensed)
- Centrioles
- Nuclear envelope (fragmenting)
- Spindle fibers (forming)
Prometaphase (Optional) | Nuclear envelope breaks down completely, allowing spindle fibers to interact with chromosomes. | – Nuclear envelope completely disappears. – Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores (protein complexes on centromeres) of chromosomes. | – Kinetochores
- Spindle fibers (attached)
Metaphase | Chromosomes align at the center (metaphase plate). | – Chromosomes are arranged single-file, ensuring equal distribution to daughter cells. – Spindle fibers connect to each sister chromatid at the kinetochore. | – Chromosomes (aligned)
- Kinetochores
- Spindle fibers (attached)
- Metaphase plate
Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles. | – Spindle fibers shorten, pulling sister chromatids apart. – Separated chromatids become individual chromosomes. | – Chromosomes (individual)
- Spindle fibers (shortening)
Telophase | Nuclear envelope reforms and chromosomes decondense. | – Nuclear envelope reassembles around each set of chromosomes at opposite poles. – Chromosomes unwind and become less visible. | – Nuclear envelope (reforming)
- Chromosomes (decondensing)
Cytokinesis | Cell membrane pinches inward, dividing the cytoplasm and organelles into two daughter cells. | – A cleavage furrow forms at the cell equator, pinching the cell membrane inward. – Cytoplasm and organelles are distributed roughly equally between the two daughter cells. | – Cleavage furrow
Additional Notes:
- Mitosis is responsible for animal growth, development, tissue repair, and cell replacement.
- Centrioles are organelles that help organize the spindle fibers during mitosis.
This chart provides a foundational understanding of mitosis in animals. You can create a visual representation based on this information to enhance learning.



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.